Understanding Cloud IT Security: An Essential Guide
By
Lakshmeesha P Kadasur
—
min read



The cloud is a transformative force that empowers organizations with unprecedented scalability, and flexibility. Businesses are increasingly migrating their operations to the cloud. But that has brought a cybersecurity challenge that demands a strategic and proactive approach to protect their assets.
Imagine the consequences of a cyber attack crippling your cloud-based applications and services. According to IBM's Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023, the average cost of a data breach in the cloud was $4.45 million. The financial losses, operational disruptions, and reputational damage will be devastating, compromising the foundation of your organization's digital transformation journey.
In this blog, we dive into the world of cloud IT security, exploring the knowledge and insights to navigate the unique complexities of securing your cloud environments.
From understanding the shared responsibility model and mitigating the risks associated with cloud computing to exploring the security features offered by industry-leading providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure, this resource empowers you to make informed decisions and implement strong measures tailored to your organization's needs.

This article serves as a blueprint for building a resilient and future-proof cloud security posture. Gain a deep understanding of the threats, risks, and protections that shape the cloud security landscape, and unlock the full potential of cloud computing while protecting your most valuable assets.
Embrace the power of the cloud with confidence and peace of mind. Contact our team today to learn how we can partner with you in developing a comprehensive cloud IT security strategy that aligns with your business objectives and ensures the long-term success of your digital transformation initiatives.
What is Cloud IT Security?
Overview of Cloud Security in IT
With increasing adoption of cloud computing for its scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring the security of cloud environments has become a top priority. Cloud IT security refers to the practices, policies, and technologies employed to protect cloud-based systems, applications, and data from potential threats and unauthorized access.
Cloud computing has various cloud service models - Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each of these models presents unique security challenges and requires tailored security measures to protect sensitive information and maintain business continuity.
Cloud security comprises a wide range of measures, such as identity and access management, data encryption, network security, and compliance with industry regulations. It involves securing not only the cloud infrastructure but also the applications and data hosted within the cloud environment, as well as the communication channels between the cloud and on-premises systems.
Effective cloud security strategies are crucial for organizations to negate risks associated with cyber threats, data breaches, and regulatory non-compliance. By implementing strong cloud security measures, businesses can ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their critical assets.
Learn more about implementing cloud security measures in our detailed blog.
Differences Between IT Security and Cloud Security
While traditional IT security and cloud security share some fundamental principles, there are distinct differences.
Shared Responsibility Model
In cloud environments, the responsibility for security is shared between the cloud service provider and the customer. The cloud provider is responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure, while the customer is responsible for securing their applications, data, and access management.
Distributed Architecture
Cloud computing relies on distributed architectures, with resources and data distributed across multiple locations and servers. This distributed nature creates unique security challenges, such as ensuring data consistency, maintaining secure connections, and managing access controls across different components.
Dynamic Scalability
One of the benefits of cloud computing is the ability to rapidly scale resources up or down based on demand. This dynamic scalability also poses security challenges, as you must ensure that your security measures can adapt to changes in the cloud environment without compromising protection.
Data Residency and Compliance
With data stored in the cloud, your organization must consider data residency laws and industry-specific compliance regulations, which may vary across different geographical locations and jurisdictions.
Third-Party Dependencies
Cloud environments often involve third-party services and integrations, increasing the chances of security vulnerabilities and risks related to the supply chain and vendor management.
Understanding these differences is crucial to develop effective cloud security strategies and ensure that your cloud environments are adequately protected against emerging threats and risks.
Key Concepts in Cloud Security: Threats, Risks, and Protections
Cloud security revolves around three key concepts: threats, risks, and protections. Understanding these concepts is essential to have a stringent security posture in your cloud environment.
Threats: Cloud environments face various threats, including cyber attacks, data breaches, insider threats, and malicious activities. Common threats include distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, advanced persistent threats (APTs), and vulnerabilities in cloud services or applications.
Risks: The potential for threats to exploit vulnerabilities and cause harm to an organization's assets, operations, or reputation is a risk. Risks arise from inadequate access controls, misconfigured security settings, lack of encryption, or non-compliance with regulations.
Protections: The measures, controls, and technologies implemented to mitigate threats and risks are protection. These include firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), encryption techniques, identity and access management (IAM) solutions, and continuous monitoring and logging.
Effective cloud security requires you to identify and understand the threats you may face, assess the associated risks, and implement appropriate protections to protect your cloud environment. It involves a continuous process of risk assessment, security monitoring, and proactive measures to stay ahead of emerging threats and evolving attack vectors.
By combining a deep understanding of cloud security concepts with resilient security practices and technologies, you can navigate the complexities of cloud computing while protecting your valuable data and assets.
Common Cloud Security Challenges
The Biggest Threats to Security in Cloud Environments
Migrating the business operations to the cloud can create a range of security threats that can compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data and systems. Some of the biggest threats to security in cloud environments include:
Data Breaches
One of the most significant threats in cloud computing is the risk of data breaches, where sensitive information, such as customer data, intellectual property, or financial records, is accessed or stolen by unauthorized individuals or entities. Data breaches can result from various factors, including misconfigured access controls, insecure APIs, or exploitation of vulnerabilities in cloud services or applications.
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
Cloud environments are susceptible to DDoS attacks, where an attacker attempts to overwhelm cloud resources with excessive traffic, leading to service disruptions and potential data loss or theft. DDoS attacks can be particularly damaging in cloud environments due to the shared infrastructure and the potential for resource exhaustion.
According to Cloudflare's DDoS Threat Report for Q3 2023, there was an 85% year-over-year increase in volumetric DDoS attacks.

Insider Threats
While cloud providers implement strict security measures, insider threats from rogue employees or malicious insiders within the provider's organization can pose a significant risk to cloud environments. These threats can range from unauthorized access to data or systems to intentional sabotage or theft of sensitive information.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
Sophisticated and targeted cyber attacks known as APTs can pose significant challenges to cloud security. These attacks often involve highly skilled attackers who employ advanced techniques to gain unauthorized access and maintain a persistent presence within the cloud environment, potentially leading to data exfiltration or system compromise.
Misconfiguration and Human Error
Cloud environments rely heavily on proper configuration and management of security settings. Misconfigured security controls or human errors in managing cloud resources can inadvertently expose sensitive data or create vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers.
Compliance and Regulatory Risks
Organizations operating in regulated industries, such as healthcare, finance, or government, must comply with specific data protection and privacy regulations. Failure to maintain compliance in cloud environments can result in significant fines, legal implications, and reputational damage.

Understanding and mitigating these threats is crucial for organizations to establish a robust cloud security posture and protect their valuable assets in the cloud.
Downsides and Risks Associated with Cloud Security
While cloud computing offers numerous benefits, you must also consider the potential downsides and risks associated with cloud security.
Shared Responsibility: In cloud environments, the responsibility for security is shared between the cloud service provider and the customer. Misunderstandings or gaps in this shared responsibility model can lead to security vulnerabilities and potential data breaches.
Loss of Control: By outsourcing infrastructure and services to a cloud provider, you may experience a perceived loss of control over your data and systems. This can raise concerns about data sovereignty, regulatory compliance, and the ability to respond effectively to security incidents.
Vendor Lock-in: Migrating to a specific cloud service provider can result in vendor lock-in, making it challenging and costly to switch to alternative providers or bring operations back on-premises. This dependence on a single vendor can introduce security risks and limit your ability to adapt to changing security requirements.
Data Residency and Privacy Concerns: Cloud providers often store and process data in multiple geographic locations, which can raise concerns about data residency and compliance with local privacy regulations. Ensure that the cloud providers adhere to relevant data protection laws and maintain appropriate security controls.
Potential for Malicious Insider Threats: While cloud providers implement strict security measures, you cannot eliminate the potential for malicious insiders within the provider's organization. This risk highlights the importance of strict access controls, auditing, and monitoring processes.
Complexity and Skill Gaps: Effective cloud security requires specialized skills and knowledge, which can lead to skill gaps within organizations. The complexity of cloud environments and the rapid pace of technological change can make it challenging to maintain a skilled workforce capable of managing cloud security effectively.
Once you understand these downsides and risks, you can proactively address potential security vulnerabilities, implement appropriate risk mitigation strategies, and make informed decisions about your cloud security posture.
Looking to master cloud security strategies for your business. You'll find the resources and insights from our blog to be useful.
Introduction to Major Cloud Security Providers
Security Features of AWS and Azure Cloud Services
When it comes to cloud security, the two dominant players in the market are Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure. Both these cloud service providers offer dependable security features and tools to help you protect your cloud environments from various threats.
AWS Security Features
AWS offers a comprehensive set of security services and features to help you secure your cloud infrastructure, applications, and data. Some of the key security offerings from AWS include:
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM enables you to manage access to AWS services and resources securely. It allows creating and managing users, groups, and roles with granular permissions.
AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): VPC allows you to create a logically isolated section of the AWS Cloud, enabling you to launch resources in a virtual network that you define and control.
AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF): AWS WAF is a web application firewall that helps protect web applications from common web exploits like SQL injection and cross-site scripting.
AWS Shield: AWS Shield is a managed Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) protection service that protects applications running on AWS from DDoS attacks.
AWS Key Management Service (KMS): AWS KMS is a secure and resilient service for creating and managing cryptographic keys. It allows you to control and audit the use of encryption across a wide range of AWS services and in their applications.
Amazon GuardDuty: GuardDuty is a threat detection service that continuously monitors for malicious activity and unauthorized behavior to protect AWS accounts and workloads.
Microsoft Azure Security Features
Microsoft Azure also offers a comprehensive set of security services and features to help you secure your cloud environment. Here are some of the key security offerings from Azure.
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD): Azure AD is a cloud-based identity and access management service that helps secure access to Azure resources and applications.
Azure Virtual Network: Azure Virtual Network allows customers to create their own private network environment in the cloud, enabling them to securely connect Azure resources to each other and to on-premises networks.
Azure Firewall: Azure Firewall is a managed, cloud-based network security service that protects Azure Virtual Network resources from unauthorized access.
Azure DDoS Protection: Azure DDoS Protection is a service that helps protect Azure resources from Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
Azure Key Vault: Azure Key Vault is a secure and centralized cloud service for storing and managing cryptographic keys and secrets used by cloud applications and services.
Azure Security Center: Azure Security Center is a unified infrastructure security management system that provides advanced threat protection across hybrid cloud workloads.
Both AWS and Azure offer a wide range of security services and features to help customers secure their cloud environments. But the specific services and features used will depend on your security requirements, cloud architecture, and workloads.
Comparing Security Across Different Cloud Services
While AWS and Azure are the dominant players in the cloud security market, there are other cloud service providers that offer security features as well. Evaluate and compare the security offerings of different cloud providers to determine which one best fits your organization's needs.
These are some key factors to consider when comparing cloud security across different providers.
Compliance and Certifications
Evaluate the compliance standards and certifications that the cloud provider adheres to, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, ISO 27001, and others relevant to your industry or organization.
Data Encryption and Key Management
Assess the data encryption and key management capabilities offered by the cloud provider, including support for encryption at rest and in transit, as well as the ability to bring your own encryption keys.
Identity and Access Management
Evaluate the identity and access management (IAM) features offered by the cloud provider, including support for multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and integration with existing identity management systems.
Network Security
Consider the network security features offered by the cloud provider, such as virtual private clouds (VPCs), firewalls, and DDoS protection.
Monitoring and Logging
Assess the monitoring and logging capabilities offered by the cloud provider, including the ability to centralize logs, set up alerts, and integrate with existing security information and event management (SIEM) systems.
Incident Response and Disaster Recovery
Evaluate the cloud provider's incident response and disaster recovery capabilities, including their ability to quickly respond to and mitigate security incidents, as well as their data backup and recovery options.
Support and Documentation
Consider the level of support and documentation provided by the cloud provider, including access to security experts, knowledge base articles, and training resources.
It's important to thoroughly evaluate and compare the security offerings of different cloud providers to ensure that your organization's security requirements are met. Additionally, it's recommended to regularly review and update your cloud security measures as new threats and best practices emerge.
How Arche AI Can Help
Navigating the complex world of cloud IT security can be daunting, but you don't have to go it alone. At Arche, we understand the unique challenges and risks associated with cloud environments, and we're here to help you safeguard your organization's data and systems.
Our team of cloud security experts has extensive experience working with leading cloud service providers, such as AWS and Azure. We stay up-to-date with the latest security features and best practices, ensuring that you benefit from the most effective and innovative solutions.
Arche offers comprehensive cloud security services, including risk assessments, security architecture design, and implementation support. We'll work closely with you to understand your specific requirements and tailor our solutions to meet your organization's needs.
Partner with Arche and experience the peace of mind that comes with robust cloud IT security. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step toward securing your cloud infrastructure.
Written by
Lakshmeesha P Kadasur
Chief Delivery Officer
Lakki, a global modernizer for 28 years, propels digital migrations. As an automation ace and revered infrastructure sensei, he spearheads our managed services ascent, optimizing, innovating, and bending space-time with cloud initiatives. Lakki's collaborative leadership manifests new realities, guiding executives beyond virtualized mobility and mainframe milestones. With allegiances to revolutionaries like IBM, Wipro, and CTS, his transitional vision elevates companies worldwide.
BLOGS
Data Center


Mastering Data Center Management with Expert Consulting
Aug 14, 2024
—
13 min read
Data Center


Engaging with Data Center Consultants for Optimal Solutions
Aug 14, 2024
—
12 min read
Data Center


Introduction to Data Center Certifications: An Overview
Aug 14, 2024
—
14 min read
Data Center


Mastering Data Center Operations with Advanced Certifications
Aug 14, 2024
—
12 min read
Ready to take your company to the next level?
Transformation starts here, talk to our experts

© Copyright 2024 Arche AI Pvt. Ltd.
Ready to take your company to the next level?
Transformation starts here, talk to our experts

© Copyright 2024 Arche AI Pvt. Ltd.
Ready to take your company to the next level?
Transformation starts here, talk to our experts

© Copyright 2024 Arche AI Pvt. Ltd.
Ready to take your company to the next level?
Transformation starts here, talk to our experts

© Copyright 2024 Arche AI Pvt. Ltd.
BLOG
Understanding Cloud IT Security: An Essential Guide
BY
Lakshmeesha P Kadasur
—
10
min read


The cloud is a transformative force that empowers organizations with unprecedented scalability, and flexibility. Businesses are increasingly migrating their operations to the cloud. But that has brought a cybersecurity challenge that demands a strategic and proactive approach to protect their assets.
Imagine the consequences of a cyber attack crippling your cloud-based applications and services. According to IBM's Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023, the average cost of a data breach in the cloud was $4.45 million. The financial losses, operational disruptions, and reputational damage will be devastating, compromising the foundation of your organization's digital transformation journey.
In this blog, we dive into the world of cloud IT security, exploring the knowledge and insights to navigate the unique complexities of securing your cloud environments.
From understanding the shared responsibility model and mitigating the risks associated with cloud computing to exploring the security features offered by industry-leading providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure, this resource empowers you to make informed decisions and implement strong measures tailored to your organization's needs.

This article serves as a blueprint for building a resilient and future-proof cloud security posture. Gain a deep understanding of the threats, risks, and protections that shape the cloud security landscape, and unlock the full potential of cloud computing while protecting your most valuable assets.
Embrace the power of the cloud with confidence and peace of mind. Contact our team today to learn how we can partner with you in developing a comprehensive cloud IT security strategy that aligns with your business objectives and ensures the long-term success of your digital transformation initiatives.
What is Cloud IT Security?
Overview of Cloud Security in IT
With increasing adoption of cloud computing for its scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring the security of cloud environments has become a top priority. Cloud IT security refers to the practices, policies, and technologies employed to protect cloud-based systems, applications, and data from potential threats and unauthorized access.
Cloud computing has various cloud service models - Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each of these models presents unique security challenges and requires tailored security measures to protect sensitive information and maintain business continuity.
Cloud security comprises a wide range of measures, such as identity and access management, data encryption, network security, and compliance with industry regulations. It involves securing not only the cloud infrastructure but also the applications and data hosted within the cloud environment, as well as the communication channels between the cloud and on-premises systems.
Effective cloud security strategies are crucial for organizations to negate risks associated with cyber threats, data breaches, and regulatory non-compliance. By implementing strong cloud security measures, businesses can ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their critical assets.
Learn more about implementing cloud security measures in our detailed blog.
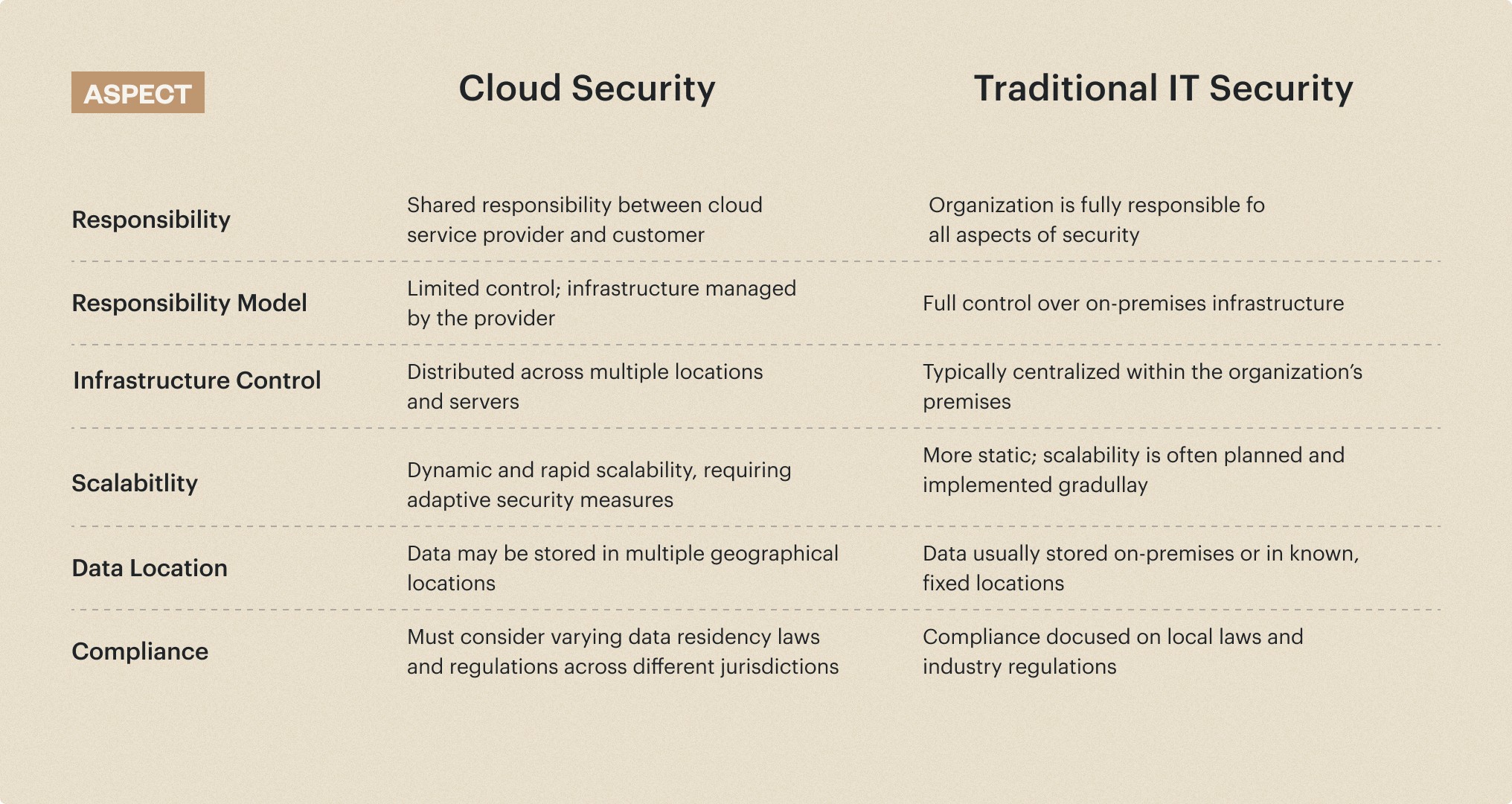
Differences Between IT Security and Cloud Security
While traditional IT security and cloud security share some fundamental principles, there are distinct differences.
Shared Responsibility Model
In cloud environments, the responsibility for security is shared between the cloud service provider and the customer. The cloud provider is responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure, while the customer is responsible for securing their applications, data, and access management.
Distributed Architecture
Cloud computing relies on distributed architectures, with resources and data distributed across multiple locations and servers. This distributed nature creates unique security challenges, such as ensuring data consistency, maintaining secure connections, and managing access controls across different components.
Dynamic Scalability
One of the benefits of cloud computing is the ability to rapidly scale resources up or down based on demand. This dynamic scalability also poses security challenges, as you must ensure that your security measures can adapt to changes in the cloud environment without compromising protection.
Data Residency and Compliance
With data stored in the cloud, your organization must consider data residency laws and industry-specific compliance regulations, which may vary across different geographical locations and jurisdictions.
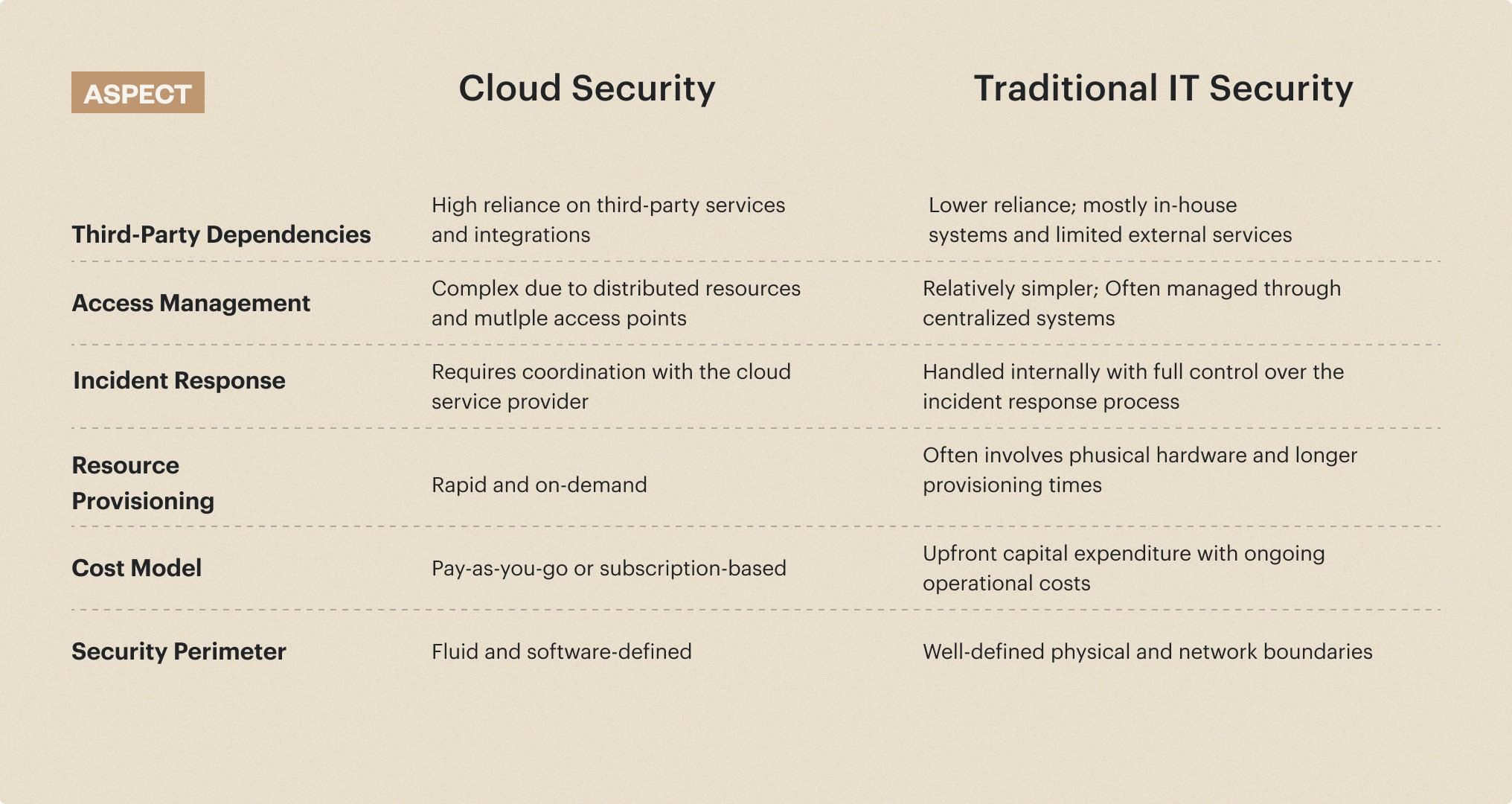
Third-Party Dependencies
Cloud environments often involve third-party services and integrations, increasing the chances of security vulnerabilities and risks related to the supply chain and vendor management.


Understanding these differences is crucial to develop effective cloud security strategies and ensure that your cloud environments are adequately protected against emerging threats and risks.
Key Concepts in Cloud Security: Threats, Risks, and Protections
Cloud security revolves around three key concepts: threats, risks, and protections. Understanding these concepts is essential to have a stringent security posture in your cloud environment.
Threats: Cloud environments face various threats, including cyber attacks, data breaches, insider threats, and malicious activities. Common threats include distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, advanced persistent threats (APTs), and vulnerabilities in cloud services or applications.
Risks: The potential for threats to exploit vulnerabilities and cause harm to an organization's assets, operations, or reputation is a risk. Risks arise from inadequate access controls, misconfigured security settings, lack of encryption, or non-compliance with regulations.
Protections: The measures, controls, and technologies implemented to mitigate threats and risks are protection. These include firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), encryption techniques, identity and access management (IAM) solutions, and continuous monitoring and logging.
Effective cloud security requires you to identify and understand the threats you may face, assess the associated risks, and implement appropriate protections to protect your cloud environment. It involves a continuous process of risk assessment, security monitoring, and proactive measures to stay ahead of emerging threats and evolving attack vectors.
By combining a deep understanding of cloud security concepts with resilient security practices and technologies, you can navigate the complexities of cloud computing while protecting your valuable data and assets.
Common Cloud Security Challenges
The Biggest Threats to Security in Cloud Environments
Migrating the business operations to the cloud can create a range of security threats that can compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data and systems. Some of the biggest threats to security in cloud environments include:
Data Breaches
One of the most significant threats in cloud computing is the risk of data breaches, where sensitive information, such as customer data, intellectual property, or financial records, is accessed or stolen by unauthorized individuals or entities. Data breaches can result from various factors, including misconfigured access controls, insecure APIs, or exploitation of vulnerabilities in cloud services or applications.
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
Cloud environments are susceptible to DDoS attacks, where an attacker attempts to overwhelm cloud resources with excessive traffic, leading to service disruptions and potential data loss or theft. DDoS attacks can be particularly damaging in cloud environments due to the shared infrastructure and the potential for resource exhaustion.
According to Cloudflare's DDoS Threat Report for Q3 2023, there was an 85% year-over-year increase in volumetric DDoS attacks.

Insider Threats
While cloud providers implement strict security measures, insider threats from rogue employees or malicious insiders within the provider's organization can pose a significant risk to cloud environments. These threats can range from unauthorized access to data or systems to intentional sabotage or theft of sensitive information.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
Sophisticated and targeted cyber attacks known as APTs can pose significant challenges to cloud security. These attacks often involve highly skilled attackers who employ advanced techniques to gain unauthorized access and maintain a persistent presence within the cloud environment, potentially leading to data exfiltration or system compromise.
Misconfiguration and Human Error
Cloud environments rely heavily on proper configuration and management of security settings. Misconfigured security controls or human errors in managing cloud resources can inadvertently expose sensitive data or create vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers.
Compliance and Regulatory Risks
Organizations operating in regulated industries, such as healthcare, finance, or government, must comply with specific data protection and privacy regulations. Failure to maintain compliance in cloud environments can result in significant fines, legal implications, and reputational damage.

Understanding and mitigating these threats is crucial for organizations to establish a robust cloud security posture and protect their valuable assets in the cloud.
Downsides and Risks Associated with Cloud Security
While cloud computing offers numerous benefits, you must also consider the potential downsides and risks associated with cloud security.
Shared Responsibility: In cloud environments, the responsibility for security is shared between the cloud service provider and the customer. Misunderstandings or gaps in this shared responsibility model can lead to security vulnerabilities and potential data breaches.
Loss of Control: By outsourcing infrastructure and services to a cloud provider, you may experience a perceived loss of control over your data and systems. This can raise concerns about data sovereignty, regulatory compliance, and the ability to respond effectively to security incidents.
Vendor Lock-in: Migrating to a specific cloud service provider can result in vendor lock-in, making it challenging and costly to switch to alternative providers or bring operations back on-premises. This dependence on a single vendor can introduce security risks and limit your ability to adapt to changing security requirements.
Data Residency and Privacy Concerns: Cloud providers often store and process data in multiple geographic locations, which can raise concerns about data residency and compliance with local privacy regulations. Ensure that the cloud providers adhere to relevant data protection laws and maintain appropriate security controls.
Potential for Malicious Insider Threats: While cloud providers implement strict security measures, you cannot eliminate the potential for malicious insiders within the provider's organization. This risk highlights the importance of strict access controls, auditing, and monitoring processes.
Complexity and Skill Gaps: Effective cloud security requires specialized skills and knowledge, which can lead to skill gaps within organizations. The complexity of cloud environments and the rapid pace of technological change can make it challenging to maintain a skilled workforce capable of managing cloud security effectively.
Once you understand these downsides and risks, you can proactively address potential security vulnerabilities, implement appropriate risk mitigation strategies, and make informed decisions about your cloud security posture.
Looking to master cloud security strategies for your business. You'll find the resources and insights from our blog to be useful.
Introduction to Major Cloud Security Providers
Security Features of AWS and Azure Cloud Services
When it comes to cloud security, the two dominant players in the market are Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure. Both these cloud service providers offer dependable security features and tools to help you protect your cloud environments from various threats.
AWS Security Features
AWS offers a comprehensive set of security services and features to help you secure your cloud infrastructure, applications, and data. Some of the key security offerings from AWS include:
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM enables you to manage access to AWS services and resources securely. It allows creating and managing users, groups, and roles with granular permissions.
AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): VPC allows you to create a logically isolated section of the AWS Cloud, enabling you to launch resources in a virtual network that you define and control.
AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF): AWS WAF is a web application firewall that helps protect web applications from common web exploits like SQL injection and cross-site scripting.
AWS Shield: AWS Shield is a managed Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) protection service that protects applications running on AWS from DDoS attacks.
AWS Key Management Service (KMS): AWS KMS is a secure and resilient service for creating and managing cryptographic keys. It allows you to control and audit the use of encryption across a wide range of AWS services and in their applications.
Amazon GuardDuty: GuardDuty is a threat detection service that continuously monitors for malicious activity and unauthorized behavior to protect AWS accounts and workloads.
Microsoft Azure Security Features
Microsoft Azure also offers a comprehensive set of security services and features to help you secure your cloud environment. Here are some of the key security offerings from Azure.
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD): Azure AD is a cloud-based identity and access management service that helps secure access to Azure resources and applications.
Azure Virtual Network: Azure Virtual Network allows customers to create their own private network environment in the cloud, enabling them to securely connect Azure resources to each other and to on-premises networks.
Azure Firewall: Azure Firewall is a managed, cloud-based network security service that protects Azure Virtual Network resources from unauthorized access.
Azure DDoS Protection: Azure DDoS Protection is a service that helps protect Azure resources from Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
Azure Key Vault: Azure Key Vault is a secure and centralized cloud service for storing and managing cryptographic keys and secrets used by cloud applications and services.
Azure Security Center: Azure Security Center is a unified infrastructure security management system that provides advanced threat protection across hybrid cloud workloads.
Both AWS and Azure offer a wide range of security services and features to help customers secure their cloud environments. But the specific services and features used will depend on your security requirements, cloud architecture, and workloads.
Comparing Security Across Different Cloud Services
While AWS and Azure are the dominant players in the cloud security market, there are other cloud service providers that offer security features as well. Evaluate and compare the security offerings of different cloud providers to determine which one best fits your organization's needs.
These are some key factors to consider when comparing cloud security across different providers.
Compliance and Certifications
Evaluate the compliance standards and certifications that the cloud provider adheres to, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, ISO 27001, and others relevant to your industry or organization.
Data Encryption and Key Management
Assess the data encryption and key management capabilities offered by the cloud provider, including support for encryption at rest and in transit, as well as the ability to bring your own encryption keys.
Identity and Access Management
Evaluate the identity and access management (IAM) features offered by the cloud provider, including support for multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and integration with existing identity management systems.
Network Security
Consider the network security features offered by the cloud provider, such as virtual private clouds (VPCs), firewalls, and DDoS protection.
Monitoring and Logging
Assess the monitoring and logging capabilities offered by the cloud provider, including the ability to centralize logs, set up alerts, and integrate with existing security information and event management (SIEM) systems.
Incident Response and Disaster Recovery
Evaluate the cloud provider's incident response and disaster recovery capabilities, including their ability to quickly respond to and mitigate security incidents, as well as their data backup and recovery options.
Support and Documentation
Consider the level of support and documentation provided by the cloud provider, including access to security experts, knowledge base articles, and training resources.
It's important to thoroughly evaluate and compare the security offerings of different cloud providers to ensure that your organization's security requirements are met. Additionally, it's recommended to regularly review and update your cloud security measures as new threats and best practices emerge.
How Arche AI Can Help
Navigating the complex world of cloud IT security can be daunting, but you don't have to go it alone. At Arche, we understand the unique challenges and risks associated with cloud environments, and we're here to help you safeguard your organization's data and systems.
Our team of cloud security experts has extensive experience working with leading cloud service providers, such as AWS and Azure. We stay up-to-date with the latest security features and best practices, ensuring that you benefit from the most effective and innovative solutions.
Arche offers comprehensive cloud security services, including risk assessments, security architecture design, and implementation support. We'll work closely with you to understand your specific requirements and tailor our solutions to meet your organization's needs.
Partner with Arche and experience the peace of mind that comes with robust cloud IT security. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step toward securing your cloud infrastructure.
Lakki, a global modernizer for 28 years, propels digital migrations. As an automation ace and revered infrastructure sensei, he spearheads our managed services ascent, optimizing, innovating, and bending space-time with cloud initiatives. Lakki's collaborative leadership manifests new realities, guiding executives beyond virtualized mobility and mainframe milestones. With allegiances to revolutionaries like IBM, Wipro, and CTS, his transitional vision elevates companies worldwide.
Partner with us
Unlock your business potential with our committed team driving your success.
Read these next


Data Center
Mastering Data Center Management with Expert Consulting
By leveraging the knowledge and experience of seasoned professionals, organizations can transform their data centers from cost centers into strategic assets that drive business growth.
Read now ➝


Data Center
Engaging with Data Center Consultants for Optimal Solutions
From improving energy efficiency and reducing operating costs to enhancing security and planning for future growth, the right consultant can unlock opportunities that drive business value.
Read now ➝


Data Center
Introduction to Data Center Certifications: An Overview
For both data center professionals and the facilities they manage, the lack of industry-recognized certifications can cause a chain reaction of problems. We solve the pain in this blog.
Read now ➝
Ready to take your company to the next level?
Transformation starts here, talk to our experts

© Copyright 2024 Arche AI Pvt. Ltd.
Ready to take your company to the next level?
Transformation starts here, talk to our experts

© Copyright 2024 Arche AI Pvt. Ltd.








