Mastering Cloud Security for Business Excellence
By
Lakshmeesha P Kadasur
—
min read



Cloud computing is synonymous with business agility, scalability, and innovation. But it comes with its fair share of cybersecurity risks. From data breaches and misconfiguration vulnerabilities to advanced persistent threats (APTs) and supply chain attacks, the challenges of securing dynamic cloud environments can be daunting.
Failure to implement robust cloud security measures can have devastating consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, regulatory fines, and operational disruptions.
To harness the full potential of cloud computing while protecting against evolving cyber threats, organizations must adopt a comprehensive and proactive approach to cloud security. This involves implementing advanced techniques tailored to the unique challenges of hybrid and multi-cloud environments, seamlessly integrating cloud security with existing IT infrastructures, and leveraging cutting-edge threat detection and response strategies.
At Arche, our cloud security experts have extensive experience helping global enterprises and industry leaders, such as Bangalore International Airport, Sundaram Clayton, and Textbook Corporation, secure their cloud journeys. With over 17 years of expertise in managing complex infrastructures, we offer a proven cloud security framework that encompasses:
Consistent security policies and centralized management across hybrid environments
Robust identity and access management with multi-factor authentication
Comprehensive data protection and encryption strategies
Advanced threat detection through user behavior analytics and deception technologies
Automated incident response and security orchestration
Continuous security monitoring, auditing, and compliance support
In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the intricacies of mastering cloud security, exploring advanced techniques, integrating security with existing infrastructures, and mitigating sophisticated threats. We'll also examine emerging trends shaping the future of cloud security and why cloud-based solutions are becoming the preferred choice for forward-thinking organizations.
Don't let security concerns hinder your cloud ambitions. Take the first step toward building a robust and future-proof cloud security strategy by booking a consultation with our experts today.
Advanced Cloud Security Techniques
Traditional security approaches and tools are not sufficient to address the unique challenges posed by cloud architectures, particularly in hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
To effectively protect their digital assets and ensure business continuity, organizations must embrace advanced cloud security techniques that align with their evolving IT landscapes.
New to cloud security? Here's our resource to simplify things for you.
Optimizing Cloud Security for Hybrid Environments
Hybrid cloud environments, which combine on-premises infrastructure with public and private cloud resources, are becoming increasingly common. While offering flexibility and scalability, hybrid environments also introduce additional security challenges due to the interconnectivity and data flow between different environments.
To optimize cloud security in hybrid environments, here are some of the strategies that you can follow.
Consistent Security Policies and Controls
Establish consistent security policies, controls, and governance frameworks across all environments, including on-premises, public cloud, and private cloud. This ensures a unified security posture and prevents security gaps or misconfigurations due to disparate policies.
Centralized Security Management
Implement centralized security management solutions that provide visibility and control across the entire hybrid environment. These solutions enable unified monitoring, threat detection, incident response, and policy enforcement across all cloud and on-premises resources.
Identity and Access Management Integration
Integrate identity and access management (IAM) systems to ensure consistent user authentication, authorization, and access controls across all environments. This includes support for single sign-on (SSO) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Data Protection and Encryption
Implement consistent data protection and encryption strategies across all environments. This includes encrypting data at rest and in transit, as well as implementing appropriate key management practices to maintain control over encryption keys.
Network Segmentation and Micro-segmentation
Segment networks and workloads into logical security zones based on risk profiles and access requirements. Micro-segmentation techniques, such as network virtualization and software-defined networking (SDN), can further isolate workloads and limit the attack surface within each environment.
Automated Security Orchestration
Use security orchestration and automation tools to streamline security processes, improve operational efficiency, and reduce the risk of human error. These tools can automate tasks such as configuration management, vulnerability scanning, patching, and incident response across hybrid environments.
Continuous Monitoring and Auditing
Implement continuous monitoring and auditing solutions that provide real-time visibility into security events, configurations, and compliance across all environments. Regular auditing helps identify and remediate misconfigurations or deviations from security policies.

These advanced techniques can help you effectively secure your hybrid cloud environments, maintain a consistent security posture, and reduce the risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, and other security incidents.
Integrating Cloud Security with Existing IT Infrastructures
When you migrate workloads and applications to the cloud, you must integrate cloud security measures with your existing IT infrastructures. This integration ensures a seamless and secure transition, minimizing the risk of security gaps or vulnerabilities during the migration process.
To effectively integrate cloud security with existing IT infrastructures, consider these strategies.
Legacy System Integration: Establish secure connections and data flows between cloud environments and legacy on-premises systems. This may involve implementing secure virtual private networks (VPNs), encrypted tunnels, or other secure communication channels.
Identity and Access Management Synchronization: Synchronize existing identity and access management systems with cloud-based IAM solutions. This ensures consistent user identities, permissions, and access controls across both environments, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or privilege escalation.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Integration: Integrate cloud security logs and events with existing SIEM solutions for centralized monitoring, analysis, and incident response. This provides a comprehensive view of security events across the entire IT infrastructure, including on-premises and cloud environments.
Compliance and Governance Alignment: Align cloud security controls and processes with existing compliance and governance frameworks. You’ll adhere to regulatory requirements, industry standards, and organizational policies across all environments.
Security Orchestration and Automation: Utilize security orchestration and automation tools to streamline and automate security processes across both on-premises and cloud environments. This includes tasks such as vulnerability management, patch management, and incident response.
Data Protection and Encryption Key Management: Implement consistent data protection and encryption strategies across on-premises and cloud environments. Integrate existing encryption key management systems with cloud-based key management services or implement a centralized key management solution.
Incident Response and Disaster Recovery Planning: Update incident response and disaster recovery plans to include cloud environments and ensure seamless coordination between on-premises and cloud-based recovery processes.
Security Skill Development: Invest in training and upskilling existing IT and security teams to ensure they possess the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively secure and manage hybrid IT environments that span on-premises and cloud infrastructures.
Such a holistic approach of integrating cloud security with existing IT infrastructures can help you minimize security gaps, maintain consistent security postures, and ensure a smooth transition to cloud computing. It’ll also protect your digital assets and maintain regulatory compliance.
Mitigating Advanced Security Threats
Advanced cyber threats, such as sophisticated malware, advanced persistent threats (APTs), and supply chain attacks, pose significant challenges to cloud security. Mitigating these threats requires a proactive and comprehensive approach that combines strict security controls, advanced threat detection capabilities, and effective incident response strategies.
Dealing with the Biggest Risks in Cloud Computing
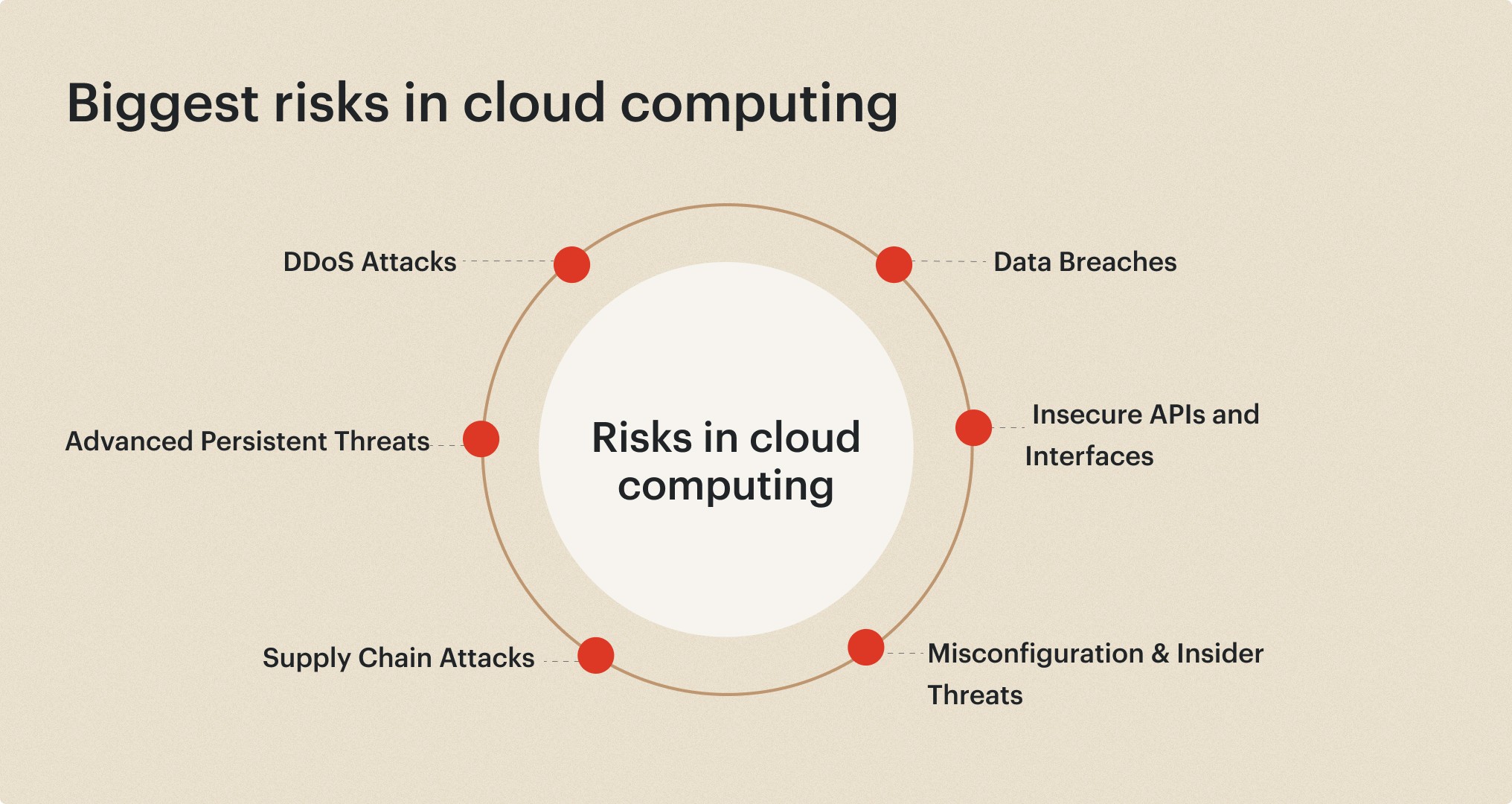
While cloud computing is beneficial, it also comes with several security risks that you must address. Some of the biggest risks in cloud computing include:
Data Breaches
The centralized nature of cloud environments makes them attractive targets for cyber criminals seeking to steal sensitive data, such as personal information, intellectual property, or financial records. Data breaches can result in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory fines.
Insecure APIs and Interfaces
Cloud services often rely on Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and web interfaces for interaction and management. Vulnerabilities in these interfaces can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access or perform malicious actions.
Misconfiguration and Insider Threats
Misconfigurations of cloud resources, such as misconfigured storage buckets or insecure access controls, can expose sensitive data or systems to unauthorized access. Additionally, insider threats, whether intentional or unintentional, can compromise cloud security.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
Cloud environments are susceptible to DDoS attacks, which can overwhelm services and disrupt business operations. These attacks can be challenging to mitigate due to the distributed nature of cloud infrastructure.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
APTs are sophisticated, targeted attacks carried out by well-resourced adversaries, such as nation-states or organized crime groups. These threats can persist within cloud environments for extended periods, gathering intelligence and compromising systems.
Supply Chain Attacks
As organizations rely on third-party services and components in their cloud environments, supply chain attacks can introduce vulnerabilities or malicious code into their systems, potentially leading to data breaches or service disruptions.
To effectively mitigate these risks, you must adopt advanced threat protection and response strategies tailored to their cloud environments.
Advanced Threat Protection and Response Strategies
A multi-layered approach with proactive security measures, continuous monitoring, and fool-proof incident response can help you combat against advanced threats. Let’s look at such strategies.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): CSPM solutions help you continuously monitor and assess the security posture of your cloud environments, identifying misconfigurations, policy violations, and potential vulnerabilities. By proactively addressing these issues, you can reduce their attack surface and mitigate risks.
Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP): CWPPs provide comprehensive security for cloud workloads, including virtual machines, containers, and serverless functions. These platforms offer features such as vulnerability management, file integrity monitoring, and behavioral analysis to detect and respond to threats targeting cloud workloads.
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB): CASBs act as intermediaries between users and cloud services, providing visibility, data security, threat protection, and compliance monitoring for cloud applications and services. CASBs can detect and prevent unauthorized access, data exfiltration, and malicious activities within cloud environments.
Deception Technologies: Deception technologies, such as honeypots and deception networks, can be deployed in cloud environments to detect and divert advanced threats. By presenting attractive targets to attackers, these technologies can lure and isolate threats, enabling organizations to study and respond to them effectively.
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): UEBA solutions use machine learning and advanced analytics to establish baselines of normal user and entity behavior within cloud environments. By detecting deviations from these baselines, UEBA can identify potential insider threats, compromised accounts, or malicious activities.

Automated Incident Response and Orchestration: Automated incident response and orchestration solutions can streamline and accelerate the response to security incidents within cloud environments. These solutions can automate tasks such as containment, investigation, and remediation, reducing the time to respond and mitigate threats.
Threat Intelligence Integration: Integrating threat intelligence feeds and services into cloud security operations can provide organizations with up-to-date information on emerging threats, vulnerabilities, and attack vectors. This intelligence can inform proactive security measures and enhance threat detection capabilities.
Security Awareness and Training: Continuously educating and training employees on cloud security best practices, recognizing phishing attempts, and handling sensitive data securely can help mitigate the risk of insider threats and human errors that could compromise cloud security.
These strategies, when deployed rightly, can protect you against advanced threats.
Yet to implement robust cloud security measures? We've written a blog that can give you clarity on it.
The Future of Cloud Security
Cloud computing is deeply integrated into business operations and the landscape of cloud security is also rapidly transforming. Emerging trends and technologies are dictating the future of cloud security.
Emerging Trends in Cloud Security
Let's look at the ever-changing emerging technologies in cloud security.
Cloud-Native Security
As cloud-native architectures and technologies like containers, serverless computing, and microservices, become mainstream, security approaches must evolve to align with them. Cloud-native security solutions are designed from the ground up to secure these dynamic and distributed environments, providing seamless integration, automated security enforcement, and scalability.
Shift to Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
CSPM solutions are gaining traction as organizations recognize the importance of continuously monitoring and assessing the security posture of their cloud environments. CSPM tools help identify misconfigurations, policy violations, and potential vulnerabilities, enabling proactive risk mitigation and compliance management.
Increased Adoption of Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP)
As cloud workloads become more complex and diverse, CWPPs are emerging as essential tools for securing virtual machines, containers, and serverless functions. These platforms offer comprehensive security features, including vulnerability management, file integrity monitoring, and behavioral analysis, tailored specifically for cloud workloads.
Integration of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Machine learning and AI are becoming increasingly common in cloud security solutions, enabling advanced threat detection, user and entity behavior analysis, and automated incident response. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of security data, identify anomalies, and adapt to evolving threat landscapes.
Emphasis on Cloud Security Automation
As cloud environments grow in scale and complexity, manual security processes become increasingly challenging and error-prone. Cloud security automation is gaining momentum, enabling organizations to streamline tasks such as configuration management, vulnerability scanning, patching, and incident response through automation tools and security orchestration platforms.
Increased Focus on Supply Chain Security
With the growing reliance on third-party services, components, and open-source software in cloud environments, supply chain security is becoming a critical concern. You can implement measures to verify the integrity of your software supply chains, monitor for vulnerabilities, and ensure secure software development practices throughout your ecosystems.
Adoption of Zero Trust Security Models
The traditional perimeter-based security model is becoming less effective in cloud environments, where resources and users can be distributed globally. Zero Trust security models, which assume that no user or device should be trusted by default, are gaining traction. These models enforce strict access controls, continuous verification, and least privilege principles, enhancing security in dynamic cloud environments.
Increased Collaboration and Shared Responsibility
Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies are becoming common. So, collaboration and shared responsibility between cloud service providers, vendors, and customers is crucial. Effective communication, clearly defined security roles, and shared best practices are essential for maintaining a robust security posture across diverse cloud environments.
Why Cloud-Based Security Solutions are the Future
Cloud-based security solutions are rapidly gaining popularity and becoming an integral part of modern security strategies. Here are some key reasons why these solutions are poised to become the future of cybersecurity:
Scalability and Elasticity: Cloud-based security solutions can dynamically scale up or down to meet changing demand, providing the flexibility to handle spikes in traffic, data volumes, or computing requirements. This scalability ensures that organizations can maintain robust security capabilities without being constrained by on-premises infrastructure limitations.
Rapid Deployment and Updates: Cloud-based security services can be rapidly deployed and updated, ensuring that organizations have access to the latest security features, threat intelligence, and protection capabilities. This eliminates the need for time-consuming on-premises software installations and updates, enabling organizations to stay ahead of emerging threats.
Global Reach and Distributed Protection: Cloud-based security solutions can provide protection and enforce policies consistently across globally distributed cloud environments and remote workforces. This distributed protection model ensures that security controls and policies are applied uniformly, regardless of location or infrastructure.
Cost-Effective and Flexible: The economies of scale offered by cloud service providers make cloud-based security solutions more cost-effective than traditional on-premises solutions, especially for organizations with limited security budgets or fluctuating resource requirements. Cloud-based services often follow a pay-as-you-go or subscription-based pricing model, providing financial flexibility.
Centralized Management and Visibility: Cloud-based security solutions offer centralized management consoles and dashboards, providing organizations with a unified view of their security posture across multiple cloud environments. This centralized visibility enables better decision-making, streamlined incident response, and more efficient security operations.
Access to Advanced Security Analytics and Intelligence: Cloud-based security providers can have vast amounts of security data, threat intelligence, and advanced analytics capabilities to enhance threat detection, response, and predictive capabilities. This expertise and scale are often difficult and costly for individual organizations to replicate on their own.
Continuous Monitoring and Compliance Support: Cloud-based security solutions can provide continuous monitoring, logging, and reporting capabilities, helping organizations maintain compliance with various security regulations and industry standards. This continuous monitoring ensures that security controls and policies are consistently enforced and any deviations are promptly detected and addressed.

How Arche AI Can Help
Mastering cloud security is essential for achieving business excellence and maintaining a competitive edge. You need a partner that understands the complexities and nuances of advanced cloud security techniques and emerging threats.
This is where Arche comes into the picture.
Our team of highly skilled cloud security experts stays ahead of the curve, continuously exploring cutting-edge technologies and strategies to fortify your cloud environment against the latest risks. We specialize in optimizing cloud security for hybrid environments, ensuring seamless integration with your existing IT infrastructures.
Arche's comprehensive cloud security services include advanced threat protection, incident response, and continuous monitoring and optimization. We'll work closely with you to develop and implement proactive security measures, ensuring that your organization stays one step ahead of cybercriminals.
Suboptimal cloud security will compromise your security posture. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and elevate your organization's cloud security posture to new heights.
Written by
Lakshmeesha P Kadasur
Chief Delivery Officer
Lakki, a global modernizer for 28 years, propels digital migrations. As an automation ace and revered infrastructure sensei, he spearheads our managed services ascent, optimizing, innovating, and bending space-time with cloud initiatives. Lakki's collaborative leadership manifests new realities, guiding executives beyond virtualized mobility and mainframe milestones. With allegiances to revolutionaries like IBM, Wipro, and CTS, his transitional vision elevates companies worldwide.
BLOGS
Data Center


Mastering Data Center Management with Expert Consulting
Aug 14, 2024
—
13 min read
Data Center


Engaging with Data Center Consultants for Optimal Solutions
Aug 14, 2024
—
12 min read
Data Center


Introduction to Data Center Certifications: An Overview
Aug 14, 2024
—
14 min read
Data Center


Mastering Data Center Operations with Advanced Certifications
Aug 14, 2024
—
12 min read
Ready to take your company to the next level?
Transformation starts here, talk to our experts

© Copyright 2024 Arche AI Pvt. Ltd.
Ready to take your company to the next level?
Transformation starts here, talk to our experts

© Copyright 2024 Arche AI Pvt. Ltd.
Ready to take your company to the next level?
Transformation starts here, talk to our experts

© Copyright 2024 Arche AI Pvt. Ltd.
Ready to take your company to the next level?
Transformation starts here, talk to our experts

© Copyright 2024 Arche AI Pvt. Ltd.
BLOG
Mastering Cloud Security for Business Excellence
BY
Lakshmeesha P Kadasur
—
14
min read


Cloud computing is synonymous with business agility, scalability, and innovation. But it comes with its fair share of cybersecurity risks. From data breaches and misconfiguration vulnerabilities to advanced persistent threats (APTs) and supply chain attacks, the challenges of securing dynamic cloud environments can be daunting.
Failure to implement robust cloud security measures can have devastating consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, regulatory fines, and operational disruptions.
To harness the full potential of cloud computing while protecting against evolving cyber threats, organizations must adopt a comprehensive and proactive approach to cloud security. This involves implementing advanced techniques tailored to the unique challenges of hybrid and multi-cloud environments, seamlessly integrating cloud security with existing IT infrastructures, and leveraging cutting-edge threat detection and response strategies.
At Arche, our cloud security experts have extensive experience helping global enterprises and industry leaders, such as Bangalore International Airport, Sundaram Clayton, and Textbook Corporation, secure their cloud journeys. With over 17 years of expertise in managing complex infrastructures, we offer a proven cloud security framework that encompasses:
Consistent security policies and centralized management across hybrid environments
Robust identity and access management with multi-factor authentication
Comprehensive data protection and encryption strategies
Advanced threat detection through user behavior analytics and deception technologies
Automated incident response and security orchestration
Continuous security monitoring, auditing, and compliance support
In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the intricacies of mastering cloud security, exploring advanced techniques, integrating security with existing infrastructures, and mitigating sophisticated threats. We'll also examine emerging trends shaping the future of cloud security and why cloud-based solutions are becoming the preferred choice for forward-thinking organizations.
Don't let security concerns hinder your cloud ambitions. Take the first step toward building a robust and future-proof cloud security strategy by booking a consultation with our experts today.
Advanced Cloud Security Techniques
Traditional security approaches and tools are not sufficient to address the unique challenges posed by cloud architectures, particularly in hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
To effectively protect their digital assets and ensure business continuity, organizations must embrace advanced cloud security techniques that align with their evolving IT landscapes.
New to cloud security? Here's our resource to simplify things for you.
Optimizing Cloud Security for Hybrid Environments
Hybrid cloud environments, which combine on-premises infrastructure with public and private cloud resources, are becoming increasingly common. While offering flexibility and scalability, hybrid environments also introduce additional security challenges due to the interconnectivity and data flow between different environments.
To optimize cloud security in hybrid environments, here are some of the strategies that you can follow.
Consistent Security Policies and Controls
Establish consistent security policies, controls, and governance frameworks across all environments, including on-premises, public cloud, and private cloud. This ensures a unified security posture and prevents security gaps or misconfigurations due to disparate policies.
Centralized Security Management
Implement centralized security management solutions that provide visibility and control across the entire hybrid environment. These solutions enable unified monitoring, threat detection, incident response, and policy enforcement across all cloud and on-premises resources.
Identity and Access Management Integration
Integrate identity and access management (IAM) systems to ensure consistent user authentication, authorization, and access controls across all environments. This includes support for single sign-on (SSO) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Data Protection and Encryption
Implement consistent data protection and encryption strategies across all environments. This includes encrypting data at rest and in transit, as well as implementing appropriate key management practices to maintain control over encryption keys.
Network Segmentation and Micro-segmentation
Segment networks and workloads into logical security zones based on risk profiles and access requirements. Micro-segmentation techniques, such as network virtualization and software-defined networking (SDN), can further isolate workloads and limit the attack surface within each environment.
Automated Security Orchestration
Use security orchestration and automation tools to streamline security processes, improve operational efficiency, and reduce the risk of human error. These tools can automate tasks such as configuration management, vulnerability scanning, patching, and incident response across hybrid environments.
Continuous Monitoring and Auditing
Implement continuous monitoring and auditing solutions that provide real-time visibility into security events, configurations, and compliance across all environments. Regular auditing helps identify and remediate misconfigurations or deviations from security policies.

These advanced techniques can help you effectively secure your hybrid cloud environments, maintain a consistent security posture, and reduce the risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, and other security incidents.
Integrating Cloud Security with Existing IT Infrastructures
When you migrate workloads and applications to the cloud, you must integrate cloud security measures with your existing IT infrastructures. This integration ensures a seamless and secure transition, minimizing the risk of security gaps or vulnerabilities during the migration process.
To effectively integrate cloud security with existing IT infrastructures, consider these strategies.
Legacy System Integration: Establish secure connections and data flows between cloud environments and legacy on-premises systems. This may involve implementing secure virtual private networks (VPNs), encrypted tunnels, or other secure communication channels.
Identity and Access Management Synchronization: Synchronize existing identity and access management systems with cloud-based IAM solutions. This ensures consistent user identities, permissions, and access controls across both environments, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or privilege escalation.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Integration: Integrate cloud security logs and events with existing SIEM solutions for centralized monitoring, analysis, and incident response. This provides a comprehensive view of security events across the entire IT infrastructure, including on-premises and cloud environments.
Compliance and Governance Alignment: Align cloud security controls and processes with existing compliance and governance frameworks. You’ll adhere to regulatory requirements, industry standards, and organizational policies across all environments.
Security Orchestration and Automation: Utilize security orchestration and automation tools to streamline and automate security processes across both on-premises and cloud environments. This includes tasks such as vulnerability management, patch management, and incident response.
Data Protection and Encryption Key Management: Implement consistent data protection and encryption strategies across on-premises and cloud environments. Integrate existing encryption key management systems with cloud-based key management services or implement a centralized key management solution.
Incident Response and Disaster Recovery Planning: Update incident response and disaster recovery plans to include cloud environments and ensure seamless coordination between on-premises and cloud-based recovery processes.
Security Skill Development: Invest in training and upskilling existing IT and security teams to ensure they possess the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively secure and manage hybrid IT environments that span on-premises and cloud infrastructures.
Such a holistic approach of integrating cloud security with existing IT infrastructures can help you minimize security gaps, maintain consistent security postures, and ensure a smooth transition to cloud computing. It’ll also protect your digital assets and maintain regulatory compliance.
Mitigating Advanced Security Threats
Advanced cyber threats, such as sophisticated malware, advanced persistent threats (APTs), and supply chain attacks, pose significant challenges to cloud security. Mitigating these threats requires a proactive and comprehensive approach that combines strict security controls, advanced threat detection capabilities, and effective incident response strategies.
Dealing with the Biggest Risks in Cloud Computing
While cloud computing is beneficial, it also comes with several security risks that you must address. Some of the biggest risks in cloud computing include:
Data Breaches
The centralized nature of cloud environments makes them attractive targets for cyber criminals seeking to steal sensitive data, such as personal information, intellectual property, or financial records. Data breaches can result in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory fines.
Insecure APIs and Interfaces
Cloud services often rely on Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and web interfaces for interaction and management. Vulnerabilities in these interfaces can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access or perform malicious actions.
Misconfiguration and Insider Threats
Misconfigurations of cloud resources, such as misconfigured storage buckets or insecure access controls, can expose sensitive data or systems to unauthorized access. Additionally, insider threats, whether intentional or unintentional, can compromise cloud security.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
Cloud environments are susceptible to DDoS attacks, which can overwhelm services and disrupt business operations. These attacks can be challenging to mitigate due to the distributed nature of cloud infrastructure.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
APTs are sophisticated, targeted attacks carried out by well-resourced adversaries, such as nation-states or organized crime groups. These threats can persist within cloud environments for extended periods, gathering intelligence and compromising systems.
Supply Chain Attacks
As organizations rely on third-party services and components in their cloud environments, supply chain attacks can introduce vulnerabilities or malicious code into their systems, potentially leading to data breaches or service disruptions.

To effectively mitigate these risks, you must adopt advanced threat protection and response strategies tailored to their cloud environments.
Advanced Threat Protection and Response Strategies
A multi-layered approach with proactive security measures, continuous monitoring, and fool-proof incident response can help you combat against advanced threats. Let’s look at such strategies.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): CSPM solutions help you continuously monitor and assess the security posture of your cloud environments, identifying misconfigurations, policy violations, and potential vulnerabilities. By proactively addressing these issues, you can reduce their attack surface and mitigate risks.
Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP): CWPPs provide comprehensive security for cloud workloads, including virtual machines, containers, and serverless functions. These platforms offer features such as vulnerability management, file integrity monitoring, and behavioral analysis to detect and respond to threats targeting cloud workloads.
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB): CASBs act as intermediaries between users and cloud services, providing visibility, data security, threat protection, and compliance monitoring for cloud applications and services. CASBs can detect and prevent unauthorized access, data exfiltration, and malicious activities within cloud environments.
Deception Technologies: Deception technologies, such as honeypots and deception networks, can be deployed in cloud environments to detect and divert advanced threats. By presenting attractive targets to attackers, these technologies can lure and isolate threats, enabling organizations to study and respond to them effectively.
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): UEBA solutions use machine learning and advanced analytics to establish baselines of normal user and entity behavior within cloud environments. By detecting deviations from these baselines, UEBA can identify potential insider threats, compromised accounts, or malicious activities.

Automated Incident Response and Orchestration: Automated incident response and orchestration solutions can streamline and accelerate the response to security incidents within cloud environments. These solutions can automate tasks such as containment, investigation, and remediation, reducing the time to respond and mitigate threats.
Threat Intelligence Integration: Integrating threat intelligence feeds and services into cloud security operations can provide organizations with up-to-date information on emerging threats, vulnerabilities, and attack vectors. This intelligence can inform proactive security measures and enhance threat detection capabilities.
Security Awareness and Training: Continuously educating and training employees on cloud security best practices, recognizing phishing attempts, and handling sensitive data securely can help mitigate the risk of insider threats and human errors that could compromise cloud security.
These strategies, when deployed rightly, can protect you against advanced threats.
Yet to implement robust cloud security measures? We've written a blog that can give you clarity on it.
The Future of Cloud Security
Cloud computing is deeply integrated into business operations and the landscape of cloud security is also rapidly transforming. Emerging trends and technologies are dictating the future of cloud security.
Emerging Trends in Cloud Security
Let's look at the ever-changing emerging technologies in cloud security.
Cloud-Native Security
As cloud-native architectures and technologies like containers, serverless computing, and microservices, become mainstream, security approaches must evolve to align with them. Cloud-native security solutions are designed from the ground up to secure these dynamic and distributed environments, providing seamless integration, automated security enforcement, and scalability.
Shift to Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
CSPM solutions are gaining traction as organizations recognize the importance of continuously monitoring and assessing the security posture of their cloud environments. CSPM tools help identify misconfigurations, policy violations, and potential vulnerabilities, enabling proactive risk mitigation and compliance management.
Increased Adoption of Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP)
As cloud workloads become more complex and diverse, CWPPs are emerging as essential tools for securing virtual machines, containers, and serverless functions. These platforms offer comprehensive security features, including vulnerability management, file integrity monitoring, and behavioral analysis, tailored specifically for cloud workloads.
Integration of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Machine learning and AI are becoming increasingly common in cloud security solutions, enabling advanced threat detection, user and entity behavior analysis, and automated incident response. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of security data, identify anomalies, and adapt to evolving threat landscapes.
Emphasis on Cloud Security Automation
As cloud environments grow in scale and complexity, manual security processes become increasingly challenging and error-prone. Cloud security automation is gaining momentum, enabling organizations to streamline tasks such as configuration management, vulnerability scanning, patching, and incident response through automation tools and security orchestration platforms.
Increased Focus on Supply Chain Security
With the growing reliance on third-party services, components, and open-source software in cloud environments, supply chain security is becoming a critical concern. You can implement measures to verify the integrity of your software supply chains, monitor for vulnerabilities, and ensure secure software development practices throughout your ecosystems.
Adoption of Zero Trust Security Models
The traditional perimeter-based security model is becoming less effective in cloud environments, where resources and users can be distributed globally. Zero Trust security models, which assume that no user or device should be trusted by default, are gaining traction. These models enforce strict access controls, continuous verification, and least privilege principles, enhancing security in dynamic cloud environments.

Increased Collaboration and Shared Responsibility
Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies are becoming common. So, collaboration and shared responsibility between cloud service providers, vendors, and customers is crucial. Effective communication, clearly defined security roles, and shared best practices are essential for maintaining a robust security posture across diverse cloud environments.
Why Cloud-Based Security Solutions are the Future
Cloud-based security solutions are rapidly gaining popularity and becoming an integral part of modern security strategies. Here are some key reasons why these solutions are poised to become the future of cybersecurity:
Scalability and Elasticity: Cloud-based security solutions can dynamically scale up or down to meet changing demand, providing the flexibility to handle spikes in traffic, data volumes, or computing requirements. This scalability ensures that organizations can maintain robust security capabilities without being constrained by on-premises infrastructure limitations.
Rapid Deployment and Updates: Cloud-based security services can be rapidly deployed and updated, ensuring that organizations have access to the latest security features, threat intelligence, and protection capabilities. This eliminates the need for time-consuming on-premises software installations and updates, enabling organizations to stay ahead of emerging threats.
Global Reach and Distributed Protection: Cloud-based security solutions can provide protection and enforce policies consistently across globally distributed cloud environments and remote workforces. This distributed protection model ensures that security controls and policies are applied uniformly, regardless of location or infrastructure.
Cost-Effective and Flexible: The economies of scale offered by cloud service providers make cloud-based security solutions more cost-effective than traditional on-premises solutions, especially for organizations with limited security budgets or fluctuating resource requirements. Cloud-based services often follow a pay-as-you-go or subscription-based pricing model, providing financial flexibility.
Centralized Management and Visibility: Cloud-based security solutions offer centralized management consoles and dashboards, providing organizations with a unified view of their security posture across multiple cloud environments. This centralized visibility enables better decision-making, streamlined incident response, and more efficient security operations.
Access to Advanced Security Analytics and Intelligence: Cloud-based security providers can have vast amounts of security data, threat intelligence, and advanced analytics capabilities to enhance threat detection, response, and predictive capabilities. This expertise and scale are often difficult and costly for individual organizations to replicate on their own.
Continuous Monitoring and Compliance Support: Cloud-based security solutions can provide continuous monitoring, logging, and reporting capabilities, helping organizations maintain compliance with various security regulations and industry standards. This continuous monitoring ensures that security controls and policies are consistently enforced and any deviations are promptly detected and addressed.

How Arche AI Can Help
Mastering cloud security is essential for achieving business excellence and maintaining a competitive edge. You need a partner that understands the complexities and nuances of advanced cloud security techniques and emerging threats.
This is where Arche comes into the picture.
Our team of highly skilled cloud security experts stays ahead of the curve, continuously exploring cutting-edge technologies and strategies to fortify your cloud environment against the latest risks. We specialize in optimizing cloud security for hybrid environments, ensuring seamless integration with your existing IT infrastructures.
Arche's comprehensive cloud security services include advanced threat protection, incident response, and continuous monitoring and optimization. We'll work closely with you to develop and implement proactive security measures, ensuring that your organization stays one step ahead of cybercriminals.
Suboptimal cloud security will compromise your security posture. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and elevate your organization's cloud security posture to new heights.
Lakki, a global modernizer for 28 years, propels digital migrations. As an automation ace and revered infrastructure sensei, he spearheads our managed services ascent, optimizing, innovating, and bending space-time with cloud initiatives. Lakki's collaborative leadership manifests new realities, guiding executives beyond virtualized mobility and mainframe milestones. With allegiances to revolutionaries like IBM, Wipro, and CTS, his transitional vision elevates companies worldwide.
Partner with us
Unlock your business potential with our committed team driving your success.
Read these next


Data Center
Mastering Data Center Management with Expert Consulting
By leveraging the knowledge and experience of seasoned professionals, organizations can transform their data centers from cost centers into strategic assets that drive business growth.
Read now ➝


Data Center
Engaging with Data Center Consultants for Optimal Solutions
From improving energy efficiency and reducing operating costs to enhancing security and planning for future growth, the right consultant can unlock opportunities that drive business value.
Read now ➝


Data Center
Introduction to Data Center Certifications: An Overview
For both data center professionals and the facilities they manage, the lack of industry-recognized certifications can cause a chain reaction of problems. We solve the pain in this blog.
Read now ➝
Ready to take your company to the next level?
Transformation starts here, talk to our experts

© Copyright 2024 Arche AI Pvt. Ltd.
Ready to take your company to the next level?
Transformation starts here, talk to our experts

© Copyright 2024 Arche AI Pvt. Ltd.








